There will only be 21 million Bitcoins in existence, forever! It is a hard cap or maximum supply and it plays a pretty large part in the valuation of any cryptocurrency.
In a centralized economy, the currency is issued by a central bank at a rate that is supposed to match the growth of the number of goods. The monetary base is controlled by a central bank, that can increase the supply by issuing more currency.
In a fully decentralized monetary system, there is no central authority that regulates the monetary base. Instead, the currency is created by the nodes of a peer-to-peer network. The Bitcoin generation algorithm defines, in advance, how the currency will be created and at what rate. Any currency that is generated by a malicious user that does not follow the rules will be rejected by the network and thus is worthless.
So, how can we be certain that there can be no more than 20 million Bitcoins? And, why cant it be changed? Read on..
Why 21 Million?
The overall supply of a coin can be broken down into 3 main parts: Circulating Supply, Total Supply, & Maximum Supply.
- Circulating Supply is the amount of coins that are actively out in circulation being traded or held. Some projects have all their coins pre-mined, some release every coin from the start, while others you have to mine the coins over time, or they are released on a schedule. Regardless, circulating supply only refers to what is available at the moment.
- Total Supply is the amount of coins that are in existence at the moment. These coins are created already, but they are not necessarily in circulation. An example would be the Federal Reserve printing a fresh batch of USD to get them ready for release. They are not yet in circulation, but would still count towards the total supply of all USD ever created.
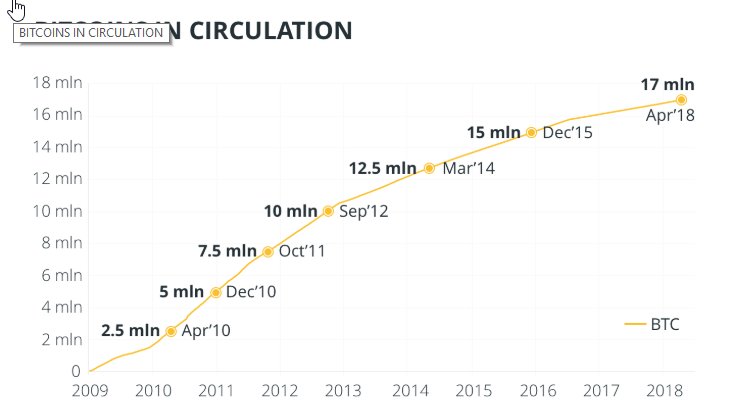
- Maximum Supply is the big one. This lets you know that a coin does in fact have a hard cap and denotes the amount of coins that will ever be in existence. In Bitcoins case, the current Circulating Supply is 17 300 900 BTC, while the Maximum Supply is 21 000 000 which leaves 3 699 100 million BTC left to come into existence through mining.
What is the maximum number of Bitcoins that will ever enter circulation? The 21 million supply cap is Bitcoin’s best-known feature. And this hard cap cannot be changed as it is part of Bitcoins core features and code. In other words, crypto inventor Satoshi Nakamoto set a monetary policy based on artificial scarcity at bitcoins inception that there would only ever be 21 million coins in total.
Technical Explanation
One of the reasons was the need to keep the number of Satoshis within the limits of 64-bit double floating numbers with a small margin for multiplication/division rounding.
64 bit floating gives 52 bits of explicit storage. Interestingly 2 to the power of 51 is 2,251,799,813,685,248 units. This is just enough to store 21 million coins times 108 divisions.
Mathematical Explanation
Calculate the number of blocks per 4-year cycle:
6 blocks per hour

Sum all the block reward sizes:
![]()
Multiply the two:
![]()
Economically, because the currency is effectively infinitely divisible, then the precise amount doesnt matter, as long as the limit remains fixed.
Since Bitcoin is often compared to gold, total coins match the total amount of gold mined in human history which can be imagined as a cube 21 m on a side.
As it is not entirely so important how many Bitcoins will exactly be mined. Satoshi could have easily chosen almost any number. He could just adjust block reward halving (210 000 blocks), reward sizes (50, 25, 12.5 ) etc. to match some particular number.
How Many Bitcoins Are Left?
The remaining coins not in circulation are in a pool dedicated to rewarding miners for maintaining the integrity of the network. As miners validate transactions and create new blocks, they receive the remaining coins from this pool as a reward. The Bitcoin source code outlines how the mining rewards should be distributed and when these distributions occur.
There are currently 17 300 900 BTC in existence. This number changes about every 10 minutes when new blocks are mined. The reward for mining each block started at 50 BTC and has since “halved” twice. The current reward sits at 12.5 Bitcoins per block.
144 blocks per day are mined on average, and there are 12.5 BTC per block. 144 x 12.5 is 1,800, so thats the average amount of new coins mined per day.
Because many miners are adding new hashpower, over the last few years blocks have often been found at 9.5-minute intervals rather than 10. This creates new coins faster, so on most days, there are actually more than 1,800 new Bitcoins created.
Nakamoto’s protocol also requires that the mining reward is halved every 210,000 blocks or approximately four years. The next miner halving will take place within two years, approximately in 2020 depending on the hash rate, bringing the rewards down to 6.25 BTC per mined block.
What Happens When 21 Million Bitcoins Are Mined?
Once miners have unlocked 21 million of Bitcoins, the planets supply will essentially be tapped out, unless Bitcoins protocol is changed to allow for a larger supply. Sceptics have even proposed that it is theoretically possible to increase Bitcoin’s hard capped supply via a 51 percent or a Sybil attack, but so far neither of these manipulations has proven feasible in the case of BTC.
After 64 total halvings, there will be no more Bitcoins left to reward miners and all 21 million BTC will be in circulation. This will occur sometime in 2140.

Right now, miners earn most of their income via the block reward. When all BTC are mined, there wont be a block reward to pay to miners. When a user sends a BTC transaction, a small fee is attached. These fees go to miners and this is what will be used to pay miners instead of the block reward, and the transaction fees should be high enough of an incentive for miners to continue running the network (transaction fees should increase dramatically).
As BTC price rises, the value of transaction fees will increase. First, because cryptocurrency becomes more valuable and second because people are willing to pay more in fees in order to get their transaction confirmed faster. However, in order for this increase to be enough for transaction fees to encourage mining on its own, the value of Bitcoin will have to increase substantially.
Bitcoin has already seen massive hikes in price in just the past few years. While no one is entirely sure the crypto-financial world, it seems likely that a limited supply of the currency may cause prices to continue to increase. There are supplies of inactive coins that are held around the world, the largest supply of which belongs to mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto. By the way, check out our awesome article about bitcoin symbol history
Conclusions
To conclude, there are several different ways that Bitcoin mining can remain profitable after the block reward goes away. However, this isn’t something we have to worry about at the moment. This is still over a century away!
Sources
Bitcoin: Benefit or Curse? George F. Hurlburt
648K-Bits About Bitcoin Nancy G. Neslund