Did you send some BTC to someone a little while ago? Maybe even a few hours ago? Is your transaction is still “unconfirmed” or “pending”? How long does it take to send Bitcoin? If you think that it should happen immediately, then perhaps you dont quite understand Bitcoin transactions. But youve come to the right place. Here you will learn about how a Bitcoin transaction works, why it takes time, and what to expect. You will get a clearer understanding of how long a Bitcoin transaction takes.
When you initiate a Bitcoin transaction, it needs to be approved by the network before it can be completed. The approval process consists of confirmations.
The Bitcoin community has set a standard of 6 confirmations that a transfer needs before it is accepted by the receiving wallet, and recognized by the entire network.
How does Bitcoin work – the basics for newbies
The blockchain is a shared public ledger on which the entire Bitcoin network relies. All confirmed operations are included in the blockchain. It allows Bitcoin wallets to calculate their spendable balance so that new transactions can be verified, thereby ensuring they’re actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the chronological order of the blockchain are enforced with cryptography.
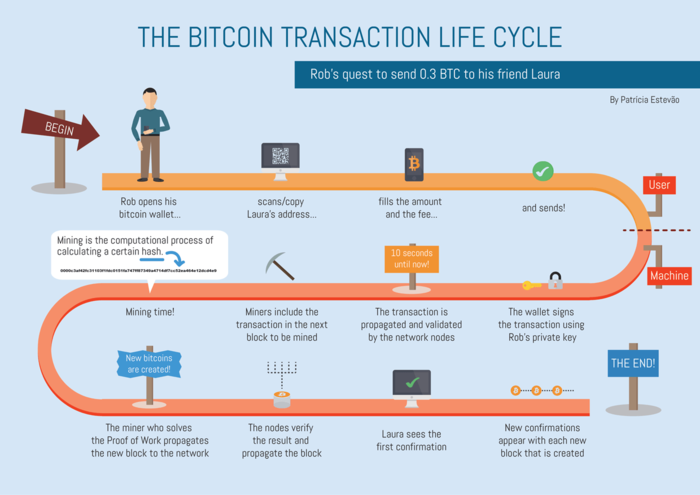
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the blockchain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key or seed, which is used to sign transactions, providing mathematical proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet. The signature also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has been issued. All operations are broadcast to the network and usually begin to be confirmed within 10-20 minutes, through a process called mining.
Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to confirm pending transactions by including them in the blockchain. It enforces a chronological order in the blockchain, protects the neutrality of the network, and allows different computers to agree on the state of the system. To be confirmed, transactions must be packed in a block that fits very strict cryptographic rules that will be verified by the network. These rules prevent previous blocks from being modified, because doing so would invalidate all subsequent blocks. Mining also creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that prevents any individual from easily adding new blocks consecutively to the blockchain.
What is a Bitcoin transaction?
When you send Bitcoin, a single data structure, namely a Bitcoin transaction, is created by your wallet client and then broadcast to the network. Bitcoin nodes on the network will relay and rebroadcast the operation, and if the transaction is valid, nodes will include it in the block they are mining. Usually, within 10-20mins, the transaction will be included, along with other operations, in a block in the blockchain. At this point, the receiver is able to see the transaction amount in their wallet.
Transaction confirmation
It seems simple: a transaction is “unconfirmed” once it has been produced and cryptographically signed, and “confirmed” once it has been successfully included in the blockchain. Keep in mind that confirmed transactions cannot be canceled.
Unfortunately, the blockchain does not offer strong consistency, understood as any data included in the blockchain is guaranteed to be included forever. For technical reasons, the blockchain features a weaker property called eventual consistency, meaning that eventually all parties will agree on the blockchain up to a certain ever-increasing prefix.
However, it is possible (although rare) for the last n blocks to be orphaned in a reorganization. This is exponentially less likely to occur the larger n gets. It typically happens multiple times a day, for example, that a single block is orphaned. But it has happened only a few dozen times in history.
In practice, the community has adopted 6 blocks as a standard confirmation period. That is, once a transaction is included in a block in the blockchain which is followed up by at least 6 additional blocks, the transaction is “confirmed.”
How long does a bitcoin transaction take?
Unfortunately, this process does not occur instantly. In fact, BTC transactions are subject to delays ranging from a few minutes to a few days. This is because Bitcoin requires miners to verify transactions. As mentioned before, operations are usually lumped into “blocks,” to be verified and added to the public blockchain, according to standard Bitcoin protocol, it takes about ten minutes to mine one block. That’s how the blockchain ensures that the money you’re sending is yours to send, it’s one of the ways they prevent fraud in the system.
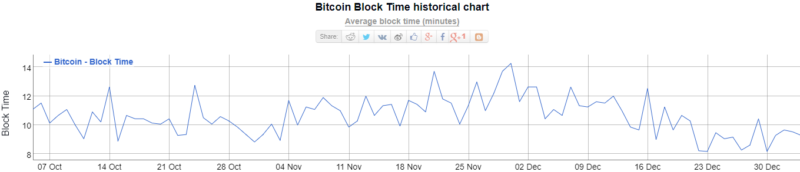
Some people would say that “one hour” is the standard BTC transaction time. But it’s not always true. Since blocks are found by a random process, there is no telling precisely how long it will take for 6 blocks to be found. On average, it takes about 10 minutes to find each block. The average block time can actually be slightly shorter or longer depending on if the total hash power of the Bitcoin network is growing or shrinking. That’s why the current BTC transaction time can take from 10 minutes to 4-6 hours for operations to be confirmed on the blockchain, depending on the Bitcoin blockchain congestion at the time you initiate your transaction.
However, due to its rising popularity, the Bitcoin network is often backlogged with transactions waiting to be lumped into a block. Block sizes are limited, and those which do not make it into one are lumped into a large queue known as the “bitcoin mempool.” The mempool fluctuates in size, with wait times also dependent on transaction priority and fees.
Average Bitcoin Transaction Time
One hour” is the common answer, but this is not quite the whole story. Because blocks are found by a random process, there is no telling precisely how long it will take for 6 blocks to be found. On average, it takes about 10 minutes to find each block. The average block time can actually be slightly shorter or longer depending on if the total hash power of the Bitcoin network is growing or shrinking. Ignoring this detail though, this is why 6 confirmations take about 1 hour on average. However, the block-creation (or mining) process is random and each block may take much longer or shorter.

This process does not occur instantaneously. In fact, bitcoin transactions are subject to delays ranging from a few minutes to a few days. This is because bitcoin requires miners to verify transactions. As it was mentioned earlier, transactions are usually lumped into blocks to be verified and added to the public blockchain, according to standard bitcoin protocol, it takes about ten minutes to mine one block.
In theory, the 10 minutes time frame is only the average time. That means the time between blocks can be 1 minute or 20 minutes, or even longer, or anything in between. Its just some mathematical variance playing into it, but the expected timeframe would be 10 minutes indeed.
Like, if you throw a coin ten times, your expected result would be 5 heads and 5 tails, but in the real world youd frequently see 6 heads 4 tails, 3 heads 7 tails and all that. If youd throw a coin a thousand times, the real world results would be closer to the expected result.
Same with blocks: if you take the times of the last, say 1000 blocks, theyd be pretty close to an average time of 10 minutes, but the single blocks within this sample size can deviate quite strongly from the expected value.
Delays could also happen in confirmations because of miners not finding a solution to the algorithm. This part is random, so sometimes it doesn’t happen 10 minutes on the dot.
However, there is a greater than 60% chance your transaction will be confirmed within 10 minutes if you pay a high enough fee.
Transaction fee
Fees are calculated by the size of the transaction. Every transaction has a size, just like a file size, and it depends on many factors. The fastest and cheapest transaction fee is currently 60 Satoshi/byte. So if, for example, your transaction is 257 bytes, you will need to pay 257*60 = 15,420 Satoshi as a transaction fee in order to be included in the next block. Most wallets today will either automatically add the required fee to get the operation confirmed as soon as possible or will let you choose from a variety of fees according to the requested Bitcoin confirmation time (e.g. fast, medium, slow).
Conclusion
We hope that this article helped you become a more confident cryptocurrency user. In a nutshell, a transaction is confirmed when it is permanently included in the Bitcoin blockchain. And there is no need to worry if it takes more than an hour before the addressee gets the BTC you sent.