If youve never heard of a Testnet, it is a testing network that allows novice traders to trade cryptocurrencies risk-free. Its a nice way to give people a way to get their hands dirty in trading, using a real-world simulation. Once they understand what they are doing, they are ready to move on to the real thing. Lets take a look at how it works.
What is a Testnet?
The testnet is an alternative Bitcoin or Ethereum block chain, to be used for testing. It is a sandbox for software developers to check that their code runs properly before they make possibly costly deployments to a mainnet. It works for both full-time blockchain developers as well as students looking to polish their skills. It also gives an opportunity for everyone to give feedback about the performance of the platform.
This type of environment provides the virtual machine, a blockchain and a faucet for test tokens so that a developer has everything he/she needs for testing and verification of their use cases without using real cryptocurrency.
As one would expect, currency stored in crypto wallets on the “regular” network is not visible on the testnet. However, it has its own set of bitcoins (Zcash, Monero, Tron or any other digital currencies), also referred to as “testnet coins”. These coins have no value whatsoever, though, and cannot be traded at any exchange. However, the coins can be used to perform test transactions, ensuring everything is working as expected.
The Bitcoin network is divided into three networks:
- The main network (mainnet) where coins are traded as real currency,
- A test network called the Testnet (where coins with no associated value are traded for testing purposes),
- A regression testing network (where coins are created instantly and are never traded to others outside the user’s network).
Coins mined in one network stay in that network, thus coins cannot be transferred between networks. It is because of this separation that we are able to use the Testnet as an environment for learning.
The primary reason why the testnet is so important is for developers and other coders to experiment with new code and solutions. In doing so, they are not “disturbing” the main bitcoin network, nor are they forced to use bitcoins which actually have a value. More importantly, if a proposed code change were to go awry, it will have no impact on the main bitcoin ecosystem. It is a pure testing environment and should always be treated as such.
Every cryptocurrency in existence has their own sandbox, all of which are actively used by developers to introduce new features. To be more specific, every developer should use the testnet availability, although not all of them may do so in the end. Every testing environment has its own wallet system to test transactions.
- BitMEX Testnet
If you would like to try trading on BitMEX, but not ready to deposit real bitcoin, you can play around with a sandbox to learn without risking real funds.
- Ethereum Testnet
Before a project launches on the Ethereum blockchain (or before changes are made to the blockchain itself), a version is deployed to an Ethereum Test Network, which simulates Ethereum. It gives developers and the community to check the use cases before real assets are involved.
The following public testnets are now available:
- Ropsten
- Rinkeby
- Kovan
- Bitshares Testnet
There is an open public testnet that has been deployed and is fully functional for anyone to use and is shared among developers, and private testnets that every developer could easily deploy at home to benefit from extra low latency and additional super powers over the network.
Testnet Coins
Both the main Bitcoin network and the Testnet network contain live blockchains and real users trading real, mined coins. Bitcoins on the main network have a real value associated with them whereas the Testnet bitcoins do not.

Test coins are given away for free to anyone that wants them. Whereas coins on the main network are traded for goods and services as any fiat currency is.
Test assets are given out for free from what are called “Faucet Websites.” These websites are set up by miners or other users with a surplus of Testnet coins. They send coins to anyone who requests them and kindly asks for their return when the user is finished with them.
Trading crypto in the test environment is exactly the same process as trading them on the main network. The process goes like this: Blocks are mined, coins are generated by the mining, users send Bitcoins to other users, the transaction is recorded in the blockchain, blocks of transactions are mined, and the process repeats. Both beginners and developers who are testing new Bitcoin-based programs use this type of assets.
The Bitcoin Testnet implementation does not require a separate installation. Bitcoin wallets that have the ability to connect to the network can be started with a special flag that will direct the software to connect to the Testnet blockchain instead of the main network blockchain.
What Is a Mainnet?
Mainnet (the main network) is the original and functional blockchain where actual transactions take place in the distributed ledger and the native cryptocurrencies have real value. It carries out the functionality of executing real transactions within the network which is stored on the blockchain and is referred to as the ‘end product’ that is open for the public to use. Launching of Mainnet is actually making the blockchain open to the public.
Each transaction executed on the blockchain requires participants to pay a transaction fee (payable in the native coin) so as to incentivize miners to validate the transactions and prevent network spamming.
Mainnet in cryptocurrencies are the final products in blockchain projects that make it possible to send and receive digital currencies. However, mainnets do undergo changes from time to time whenever project teams decide there is a need for updates or revision.
EOS Mainnet was one of the most awaited blockchain projects seen as a fast, scalable and efficient version of Ethereum. EOS is a blockchain platform for the development of decentralized applications. It is dubbed as an Ethereum killer because its underlying software provides accounts, authentication, cloud storage as well as databases and server hosting. The platform can also process millions of transactions per second.
What Is the Difference Between the Testnet and The Mainnet?
Every blockchain has mainly two networks:
- Testnet
- Mainnet
Testnets are able to show a sort of working prototype for blockchain projects. However, mainnets are a greater integral aspect of valuing a cryptocurrency’s real-world implementation.
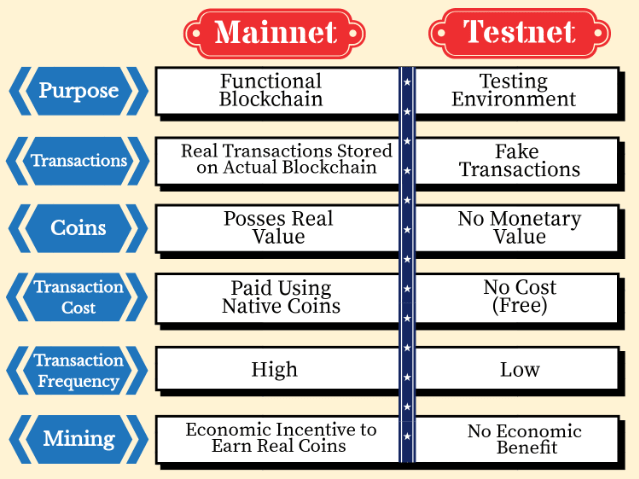
The testing network is used by developers for testing. Testnet coins are separate and distinct from actual mainnet coins, and are never supposed to have any value. This allows application developers testers to experiment, without having to use real mainnet coins.
Not all the projects have mainnets when they launch and sell their ICO’s. A lot of projects don’t even have a test network prepared during the ICO period. However, in the ideal world, this shouldn’t be the case. Before investing in an Initial Coin Offering, it is vital for an investor to ensure a blockchain project has a mainnet. The sign of a mainnet or a testnet shows how serious a project is as the two features affect the price of a cryptocurrency in one way or another.
How to avoid Testnet scams?
- If you are purchasing Bitcoin or any other crypto, please make sure the wallet you are going to receive the funds it is not a testnet wallet.
- Beware of “too good to be true” pricing or someone offering Bitcoin or Bitcoin Cash at a much lower price than the current market rate.
- Do not let the other person create a wallet for you. They might want to create a testnet wallet without your awareness and then send you testnet coins, which have no real value.
- If they tell you to create a testnet wallet to send you the funds, they are trying to scam you.
Conclusions
A testnet is often used as a testing site for development and continual enhancement of the mainnet, while the mainnet itself is the actual, functioning protocol that powers the blockchain network.

