Have you heard about the Dark Web? When you use a typical search engine, like Google, you get what seems to be a lot of results. But the truth is, what you see is only a fraction of the entire internet what is called the Surface Web. But there is much more data, and many more websites – many more than what you can find on the surface.
It is called the Dark Web (or the Darknet), and it contains all manner of things. You may have already heard of some of the controversial stuff online black markets for drugs and weapons, terrorists rings, the mercenary market, and hackers buying stolen credit card credentials and IDs. However, not every site on the Dark Web is classified as the “Darknet”. A majority of the content on the Dark Web actually isn’t illegal or immoral. Academic or library databases, for instance, are stored on the Dark Web.
A hidden Internet exists underneath the ‘surface web,’ hidden from ordinary web users. The Dark Web is intimidating. You might wonder how to find the Dark Web and what it looks like. Accessing and exploring the Darknet is relatively easy it requires no technical skills, no special invitation, and takes just a few minutes to get started.
Honestly, there are many valid reasons to go to the Dark Web checking to see if your stolen items are being sold there, to see if hackers are selling your ID or financial account information, or perhaps to see if your children or grandchildren are up to no good.
Lets find out more about the Dark Web, how it works, and how to access it.
Read on.
What is the Dark Web?
Is the Dark Web real? Yes, it is. I will try to give the definition of it and explain how it works. The underground web is a part of the internet that isn’t indexed by search engines. The Darknet websites exist on an encrypted network and cannot be found by using traditional search engines or visited by using traditional browsers when you surf the net.
Encryption is an extremely secure way of protecting your information. You can’t easily get in without passwords or biometric access, such as your fingerprint.
You might remember that Apple got into hot water with the U.S. government after the 2015 San Bernardino terrorist attacks. The attackers had an encrypted iPhone that Apple wouldn’t help the government unlock.
Encryption, when used for good, protects your location and privacy from hackers and criminals. When used for bad, as on the Dark Web, encryption can prevent the police and government from spotting illegal online activities, such as child porn, prostitution, drugs sales and more.
In recent years, the Darknet has found itself in the government’s crosshairs, with the FBI and National Security Agency (NSA) cracking down on drug merchants and pornographers. Despite a series of high-profile busts, however, this lawless realm continues to hum along, deep beneath the everyday web.
No one really knows how big the deep Web really is, but it’s hundreds (or perhaps even thousands) of times bigger that the surface Web. This data isn’t necessarily hidden on purpose. It’s just hard for current search engine technology to find it, and make sense of it.
History of the Dark Web
Who created the Dark Web? The history of the underground web goes back to the late 1960s when a student at the University of California typed out the first message between computers connected by ARPANET, the Internet progenitor developed by the Pentagon’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Within just a few years, a number of isolated, secretive networks began to appear alongside ARPANET. Some eventually became known as “Darknets.”
The modern web was born in 1980s and this is when the problem of storing sensitive or illegal data loomed large. “Data havens” became the informational analogues of tax havens, they promised to host everything from gambling operations to illegal pictures.
In late 1990s the Internet’s peer-to-peer data transmission gave birth to decentralized data hubs, some of which, like so-called top sites — where most illegal music and movie files originate — were password-protected and known only to insiders. Others, like Napster, operated in the open and facilitate millions of file transfers per day.
In 2000 software developer Ian Clarke released Freenet, revolutionary software that offered anonymous passage into the darkest reaches of the web, where one could access everything from child pornography to instructions on how to build explosives.
In 2002 researchers at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory release an early version of TOR (“The Onion Router”), which conceals the location and IP address of users who download the software. It was originally designed to protect the identity of American operatives and dissidents in repressive countries like China.
In 2005 Wired magazine estimated that the “media Darknet distributed more than half a million movies every day.” The underground network exploded into wholesale copyright infringement, from Hollywood blockbusters to Microsoft Office.
In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first Bitcoin, a form of untraceable cryptocurrency. Bitcoin used an innovative public accounting ledger that prevents double spending. Not surprisingly, the cryptocurrency turned into an instant hit in the Darknet and its anonymity made it a perfect tool for money laundering and criminal activity.
The cybersecurity and intelligence firm Procysive estimated that in 2010, the Darknet was home to “more than 50,000 extremist websites and more than 300 terrorist forums”.
In 2011, a Gawker-affiliated blog publishes an exposé on Silk Road, a hidden marketplace that “makes buying and selling illegal drugs as easy as buying used electronics.” It’s like Amazon.com for crystal meth and LSD, except only available to TOR users with Bitcoin accounts. Traffic to Silk Road surged, and the value of a Bitcoin jumped from around $10 to more than $30 within days.
In 2013, the FBI and the NSA are getting more interested in the Darknet Market. Eric Eoin Marques, one of the largest facilitators of child porn on the planet, was arrested in Dublin. His arrest coincided with a mysterious shutdown of vast swaths of the Darknet, allegedly as part of an FBI sting operation that exploited a breach in the web browser Firefox to identify TOR users.
The FBI shut down Silk Road and arrested Ross William Ulbricht, known as Dread Pirate Roberts, for allegedly masterminding the operation. The site did more than $1.2 billion in sales between 2011 and 2013, according to the indictment filed in U.S. federal court.
Despite all the efforts that the FBI and other similar agencies made to fight the Dark Web, a new anonymous marketplace called Silk Road 2.0 was back online, just over a month after the original was shut down. And in 2014 Diabolus Market, another Darknet site, rebrands itself as “Silk Road 3 Reloaded.”
How Does the Dark Web Work?
The Dark Web is a bit like the Web’s id. It’s private. It’s anonymous. It’s powerful. It unleashes human nature in all its forms, both good and bad.
The bad stuff, as always, gets most of the headlines. You can find illegal goods and activities of all kinds through the Darknet. That includes illicit drugs, child pornography, stolen credit card numbers, human trafficking, weapons, exotic animals, copyrighted media and anything else you can think of. Theoretically, you could even, say, hire a hitman to kill someone you don’t like.
But you won’t find this information with a Google search. These kinds of Web sites require you to use special software, such as The Onion Router, more commonly known as TOR.
You need to install TOR software into your browser and set up the specific connections to access a Darknet search engine. Critically, TOR is an encrypted technology that helps people maintain anonymity online. It does this in part by routing connections through servers around the world, making them much harder to track.
TOR also lets people access so-called hidden services — underground web sites for which the Dark Web is notorious. Instead of seeing domains that end in .com or .org, these hidden sites end in .onion.
As mentioned earlier, TOR was created by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory TOR for political dissidents and whistleblowers, allowing them to communicate without fear of reprisal. Since TOR was so effective in providing anonymity for these groups, it didn’t take long for the criminally-minded to start using it as well. That leaves U.S. law enforcement in the ironic position of attempting to track criminals who are using government-sponsored software to hide their trails.
In the Dark Web, users really do intentionally bury data. Often, these parts of the Web are accessible only if you use a special anonymous browser that helps peel away the onion-like layers of the Darknet.
This software maintains the privacy of both the source and the destination of data and the people who access it. For political dissidents and criminals alike, this kind of anonymity shows the immense power of the Darknet, enabling transfers of information, goods and services, legally or illegally, much to the chagrin of the powers-that-be all over the world.
Anonymity is part and parcel on the underground web, but you may wonder how any money-related transactions can happen when sellers and buyers can’t identify each other. That’s where an encrypted digital currency, Bitcoin, comes in. Like regular cash, Bitcoin is good for transactions of all kinds, and notably, it also allows for anonymity, no one can trace a purchase, legal or otherwise. And when it is paired properly with TOR, it’s perhaps the closest thing to a foolproof way to buy and sell on the Web.
Technical details
Search engines generally create an index of data by finding information that’s stored on Web sites and other online resources. This process means using automated spiders or crawlers, which locate domains and then follow hyperlinks to other domains.
This index or map is your key to finding specific data that’s relevant to your needs. Each time you enter a keyword search, results appear almost instantly thanks to that index. Without it, the search engine would literally have to start searching billions of pages from scratch every time someone wanted information, a process that would be both unwieldy and exasperating.
But search engines can’t see data stored on the deep Web. There are data incompatibilities and technical hurdles that complicate indexing efforts. There are private websites that require login passwords before you can access the contents. Crawlers can’t penetrate data that requires keyword searches on a single, specific website. There are timed-access sites that no longer allow public views once a certain time limit has passed.
There are unpublished or unlisted blog posts, picture galleries, file directories, and untold amounts of content that search engines just can’t see. And if you’re looking for a more obscure story, you may have to go directly to a specific newspaper site and then browse or search content to find what you’re looking for. This is especially true as a news story ages. The older the story, the more likely it’s stored only on the newspaper’s archive, which isn’t visible on the surface Web. Subsequently, that story may not appear readily in search engines — so it counts as part of the deep Web. The deep Web is an endless repository for a vast amount of information. There are engineering databases, financial information of all kinds, medical papers, pictures, illustrations … the list goes on.
The underground web works just about the same as the regular internet: it uses the same TCP/IP framework to transmit HTTP and FTP traffic within and between networks, over the same phone, cable or FiOS lines that carry regular internet traffic. Content on the Darknet consists of HTML webpages and their assets, just like it does on the rest of the web. First, the Dark Web isn’t indexed by search engines. Second, content on the underground web can’t be accessed with regular web browsing software alone.
The Darknet is a network of sites with encrypted content, accessible only with a secure suite of secure-browsing tools, like TOR. TOR – an acronym for the onion router — is a package of open-source security tools written for a customized version of the Mozilla Firefox browser, compatible with Windows, OS X, and Linux. The software encrypts user traffic and passes the IP address through the complex of TOR nodes.
These ‘onion layers’ help protect the user’s anonymity and provide access to similarly protected websites. These sites range from forums to wiki pages to blogs and function much like clearnet sites. Dark Web domains frequently employ non-memorable, hashed URLs with the .onion top level domain. These sites block inbound traffic from all non-secure internet connections.
Personal and work computers often house mission-critical data, like sensitive files, passwords, and health records. Because TOR can be used and the Dark Web can be accessed on a traditional home PC, security professionals rely on additional security tools like the Tails operating system. Tails is a Linux distribution that can be installed on and run from a portable flash drive. By accessing the underground web via Tails, user behavior is never logged locally, and it is significantly more challenging for malicious software to harm the host PC.
What is the Dark Web Used for?
The structure of the Darknet makes it anonymous, which means that first and foremost, it’s used for anonymous communication and web browsing. This accounts for the vast majority of network traffic through TOR. But why seek out anonymity?
Dark Side
Anonymity also brings out those who wish to do illegal things. A 2014 study found that of the different kinds of sites on the darknet, there are more markets devoted to drugs and guns than any other kind of dark site, including forums, bitcoin laundering, hacking, fraud, whistleblowing and even regular old porn.
TOR hidden services are the other thing the Dark Web does, and they’re what gives the Darknet its shady reputation. Hidden services account for only 1.5% of the TOR network volume. But the overwhelming majority of resources requested over TOR hidden services — fully 80% of that traffic — were requests from child abuse sites.
Infamous examples of Dark Web sites include the Silk Road and its offspring. The Silk Road was (and maybe still is) a website for the buying and selling of recreational drugs, besides even scarier things. For a long time, the Silk Road was the biggest name in darknet commerce. It allowed users to sell a great many illegal things, and inspired a number of similarly designed copycat markets. Transactions were conducted in bitcoins and other virtual currency, and then goods were shipped through the mail.
The Darknet made headlines in August 2015 (and many times since) after it was reported that 10GB of data stolen from Ashley Madison, a site designed to enable bored spouses to cheat on their partners, was dumped on to the Dark Web.
Hackers stole the data and threatened to upload it to the web if the site did not close down, and they eventually acted on that threat. Now the spouses of Ashley Madison users have received blackmail letters demanding they pay $2500 in Bitcoin or have their infidelity exposed.
Bright Side
Although the Darknet definitely has its ugly side, it has great potential, too. The intellectual underground web is home to alternate search engines, e-mail services, file storage, file sharing, social media, chat sites, news outlets and whistleblowing sites, as well as sites that provide a safer meeting ground for political dissidents and anyone else who may find themselves on the fringes of society.
In an age where NSA-type surveillance is omnipresent and privacy seems like a thing of the past, the Dark Web offers some relief to people who value their anonymity. Dark Web search engines may not offer up personalized search results, but they don’t track your online behavior or offer up an endless stream of advertisements, either. Bitcoin may not be entirely stable, but it offers privacy, which is something your credit card company most certainly does not.
For citizens living in countries with violent or oppressive leaders, the underground web offers a more secure way to communicate with like-minded individuals. Unlike Facebook or Twitter, which are easy for determined authorities to monitor, the Darknet provides deeper cover and a degree of safety for those who would badmouth or plot to undermine politicians or corporate overlords.
The Dark Web is used frequently by good actors for legitimate reasons. Encryption, security, and privacy are championed by news organizations, tech companies, universities, and activists in repressive regimes. The U.S. State Department helps fund the TOR project, and according to the United Nations, encryption is a fundamental human right.
How Big is the Dark Web?
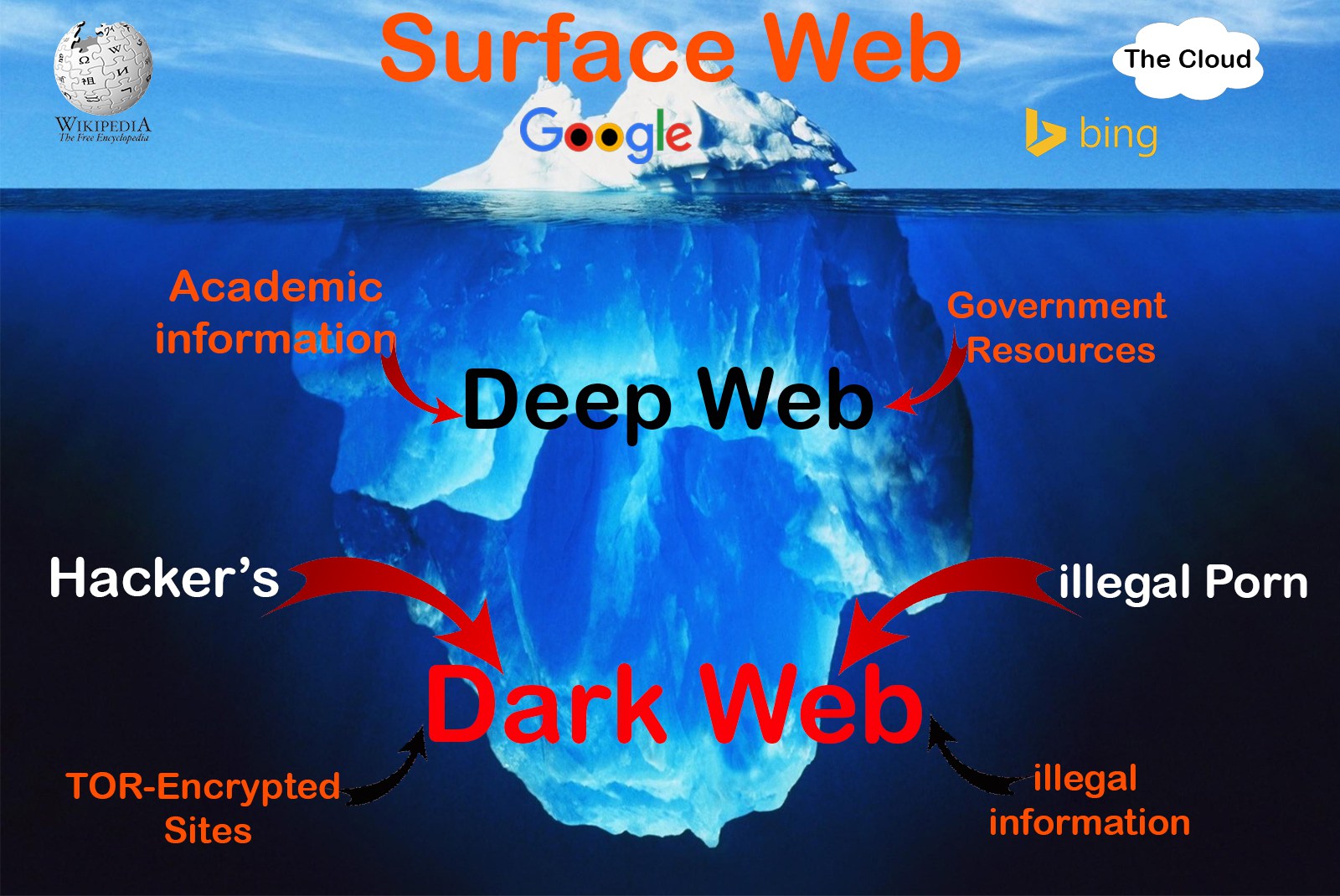
The underground web is something bigger than you can imagine. It is the part of the internet that is hidden from view. The Darknet is compared to an iceberg where you can’t predict the size of it. Only a small portion can be viewed but the rest of it is hidden.
How much of the internet is the Darknet? The Dark Web is so huge that it can’t be measured, because the majority of information is locked and hidden unlike the traditional web where you can access information from search engines.
Some specialists say that the Dark Web surface is 400 to 550 times larger than the normal web, and represents more than 90% of the internet. Almost all information is hidden in the web, and can’t be indexed, fetched, or crawled by Googlebot or any other search engines.
Deep Web vs Dark Web
What’s the difference between Deep Web and Dark Web? It’s tricky to distinguish the “dark web” from the “deep web”. Although all of these terms tend to be used interchangeably, they don’t refer to exactly the same thing. The ‘Deep Web’ refers to all web pages that search engines cannot find. There’s nothing inherently bad about the Deep Web. For example, does your company have private pages where you access information that is only for employees? If those pages aren’t registered with sites like Google, they’re hidden from view. That’s the DEEP web.
The DARK Web, which is a part of the Deep Web, is seedier. These are sites that run on an encrypted browser.
| Deep Web (Hidden Web) | Dark Web |
| The things your typical search engine can’t find (government databases, libraries, etc.) | A small portion of the deep web that is intentionally hidden and made inaccessible via search engines (the TOR network, only accessible via TOR browser) |
| That’s a huge part of the internet. | That’s a small part of the deep web. |
Dark Web Screenshots
- Silk Road
Silk Road is one of the biggest darknet markets that had ever been on the deep web. Until the arrest of its creator Ross William Ulbricht who was infamously known as DPR (Dead Pirate Roberts).
- DeepChan
A Forum on Deep Web to upload information about the selling of any goods and services.
- Hackintosh
This website offers the Best Apple/Android devices that are sold at half price.
- Onion Identity Services
This is where you can order any type of Fake ID (Passports, Driving Licenses, Citizenship etc.)
How to Access the Dark Web Safely?
Where is the Darknet? Accessing the underground requires the use of an anonymizing browser called TOR. The TOR browser routes your web page requests through a series of proxy servers operated by thousands of volunteers around the globe, rendering your IP address unidentifiable and untraceable. TOR works like magic, but the result is an experience that’s like the Darknet itself: unpredictable, unreliable and maddeningly slow. How does one get on the Dark Web? Check our brief guide that will help you navigate on the underground web:
Step 1: Start with installing a good VPN (Virtual Private Network) here and use it ALL of the time, no matter if you are on TOR or not. Open your VPN app and connect to a location other than where you are Make sure to use the OpenVPN protocol as it is the most secure.
By using the simple VPN app, your darknet activities will be hidden from your ISP and government agencies as all of your internet usage will be encrypted. No one will even know you are using TOR, let alone browsing for darknet markets. The VPN will give you a fake IP address, in another country if you like, so even if TOR is compromised then the trace just leads back to somewhere else that can’t be linked to you. The other benefit of using a VPN is to prevent hackers from stealing your identity and or personal files and photos from your computer.
Step 2:You can’t access the deep web just using a common browser like Internet Explorer or Google Chrome. To get darknet access, you will need to download the anonymous browser called TOR browser bundle from your normal favorite browser. Get it only from the official TOR website, NEVER download it from anywhere else!
Install the TOR browser bundle on your PC or Mac. When the download is complete, double-click the downloaded file, choose the destination folder (the folder where you want to extract TOR browser), and choose extract.
Step 3: Close all of your browsing windows and all apps connecting to the world wide web like Google Drive, Skype, OneDrive, iCloud etc.
Step 4: Start TOR Browser. Open the folder where you extracted TOR browser and double-click “Start Tor Browser”. The TOR start page will open in a browser window. From here, you now have a good level of anonymity and security and you are able to gain access to .onion websites through your TOR browser.
How to Use the Dark Web?
The Dark Web is not entirely malicious, but it’s also not a safe place to visit. Novices and experts alike should exercise care and caution when visiting the Darknet. ZDNet does not condone illegal or unethical activity. Offensive material can sometimes be just a click away. Browse at your own risk. Never break the law. Use the underground web safely, and for legal purposes only. Depending on what you intend to do on the Darknet, some users recommend placing tape over your laptop’s webcam to prevent prying eyes watching you.
All of this activity, this vision of a bustling marketplace, might make you think that navigating the Darknet is easy. It isn’t. The place is as messy and chaotic as you would expect when everyone is anonymous, and a substantial minority are out to scam others.
Dark Web sites look pretty much like any other site, but there are important differences. One is the naming structure. Instead of ending in .com or .co, Darknet sites end in .onion. That’s “a special-use top level domain suffix designating an anonymous hidden service reachable via the TOR network,” according to Wikipedia. Browsers with the appropriate proxy can reach these sites, but others can’t.
Darknet sites also use a scrambled naming structure that creates URLs that are often impossible to remember. For example, a popular commerce site called Dream Market goes by the unintelligible address of “eajwlvm3z2lcca76.onion.”
Many sites are set up by scammers, who constantly move around to avoid the wrath of their victims. Even commerce sites that may have existed for a year or more can suddenly disappear if the owners decide to cash in and flee with the escrow money they’re holding on behalf of customers.
The anonymous nature of the TOR network also makes it especially vulnerable to distributed denial of service attacks (DDoS), said Patrick Tiquet, Director of Security & Architecture at Keeper Security, and the company’s resident expert on the topic. “Sites are constantly changing addresses to avoid DDoS, which makes for a very dynamic environment,” he said. As a result, “The quality of search varies widely, and a lot of material is outdated.”
Dark Web Site List
How to search the underground web? Dark Web search engines exist, but even the best are challenged to keep up with the constantly shifting landscape. The experience is reminiscent of searching the web in the late 1990s. Even one of the best search engines, called Grams, returns results that are repetitive and often irrelevant to the query. Link lists like The Hidden Wiki are another option, but even indices also return a frustrating number of timed-out connections and 404 errors.
If you are looking for hidden deep web links (some also call them Dark Web links), check our list of .onion sites on the darknet:
| Name | URL | Description |
| Dream Market | http://6khhxwj7viwe5xjm.onion/ | Dream Market is a marketplace for Drugs, Digital Goods and Other Services. |
| Silk Road 3 | http://silkroad7rn2puhj.onion/ | Silk Road 3 is the Darknet’s most resilient marketplace. Products are sorted in categories. They sell Cannabis, Stimulants, Ecstasy, Opioids, Benzos, Dissociatives, Psychedelic, Prescription, and Other products. |
| Valhalla | http://valhallaxmn3fydu.onion/ | Valhalla is a marketplace for Drugs sorted in categories. There are a lot of Cannabis, Stimulants, Empathogens, Psychedelics, Opiates, Pharmacy, Dissociatives and Depressants. |
| Point / Tochka Free Market | http://tochka3evlj3sxdv.onion | Tochka is a dark market shipping to all countries. Drugs and other goods are sorted in categories. |
| Wall Street Market | http://wallstyizjhkrvmj.onion | Wall Street Market is one of the newest markets on the darknet and it particularly specializes in digital goods. |
| 0day Forum | http://qzbkwswfv5k2oj5d.onion | Forum about hacking, marketplace for Accounts, Security Services, Tutorials and Payment Systems. |
| 1 Cent PM Casino | http://cxpizstpfzlljfng.onion | 1 Cent PM Casino is a casino for bet online, you can play Poker, Roulette, Slots, Baccarat etc. |
| 1000777com | http://truth77k52rbo3ov.onion | This site is dedicated to Truthseekers. It’s main purpose is to lead seekers on to a MUCH more brighter source of information, and to help shed some light to a great deal of things happening in this very mad world. |
What Can You Buy on the Dark Web?
Darknet commerce sites have the same features as any e-retail operation, including ratings/reviews, shopping carts and forums, but there are important differences. One is quality control. When both buyers and sellers are anonymous, the credibility of any ratings system is dubious. Ratings are easily manipulated, and even sellers with long track records have been known to suddenly disappear with their customers’ crypto-coins, only to set up shop later under a different name.
Most e-commerce providers offer some kind of escrow service that keeps customer funds on hold until the product has been delivered. However, in the event of a dispute don’t expect service with a smile. It’s pretty much up to the buyer and the seller to duke it out.
Even completing a transaction is no guarantee that the goods will arrive as they need to cross international borders, and customs officials are cracking down on suspicious packages. The Dark Web news site Deep.Dot.Web teems with stories of buyers who have been arrested or jailed for attempted purchases.
The Darknet marketplaces are like a shady equivalent of Aladdin’s cave – offering guns, drugs, illegal services, fake goods, and malware. It must be noted that the Dark Web not only plays host to a variety of illegal marketplaces, but is also used to distribute illegal material. Cryptalker in no way endorses these aspects of the underground web, and reminds us that most items shown below are highly illegal.
- Fake D&G jeans
- Erection pills
- Facebook hacking
- Fake driver’s license
- Guns
- Drugs
How to Use Bitcoin on the Dark Web?
Why is Bitcoin used on the underground web? The Dark Web has flourished thanks to Bitcoin, the cryptocurrency that enables two parties to conduct a trusted transaction without knowing each other’s identity. “Bitcoin has been a major factor in the growth of the Dark Web, and the Dark Web has been a big factor in the growth of Bitcoin.”
Nearly all Darknet commerce sites conduct transactions in bitcoin or some variant, but that doesn’t mean it’s safe to do business there. The inherent anonymity of the place attracts scammers and thieves, but what do you expect when buying guns or drugs is your objective?
So if you are on the underground web to buy something, then you will need to use cryptocurrency to do so and Bitcoin is the most used crypto on the Darknet. But you should be really careful to not get under the radar and not have your crypto exchange account shut down and lose money.
NEVER send cryptocurrency directly from your exchange account (where you buy the coins) to a market or anywhere on the Darknet, also never send coins directly from anywhere on the darknet to your exchange. They are onto this right away as they can tell where the coins came from, and they WILL shut you down and you will be recorded in a list for sure.
Bitcoin allows you to create a wallet without revealing your identity, but it is not entirely anonymous. All payments which have ever been made are stored on a public blockchain that anybody can view. If you want to be really safe, therefore, it is best to use a mixing service when transferring coins to your marketplace shopping wallet. This makes it more difficult for an investigator to tell where the coins came from. These services are very simple to use – instead of sending your coins directly to the deposit address for your marketplace account, you just give the deposit address to the mixing service and they provide you with a new address to send the payment to – they then do their magic before passing on new ‘clean’ coins that can’t be traced back to you. They will usually charge you a couple of percent on each transaction for providing this service.
Best Bitcoin Wallet for Dark Web
If you are going to use your Bitcoin inside the Darknet, you should transfer the coins from your exchange to a wallet. Storing your cryptocurrency in a wallet minimizes the risk of your funds being stolen by hackers and protects your anonymity.
So when choosing a wallet, the very first thing you need to do is to take privacy into consideration. Using an anonymous wallet separates your personal information from your funds, preventing anyone from tracking you down to get a slice of that sweet, crypto pie.
Surprisingly, there aren’t many wallets that focus on keeping you anonymous.
Samourai is one of the newest anonymous wallets available. Unfortunately, the product is currently just in alpha, and you can only use it if you have an Android phone.
Each time you receive bitcoin, the wallet produces a new address to prevent someone tracking your purchase habits. It also notifies you when sending bitcoin to the same address multiple times in order to deter unintentional address reuse. The wallet also includes other common privacy features such as TOR and VPN support, as well as blockchain obfuscation.
To expand the anonymity to your phone, Samourai also has a stealth mode. This cool functionality hides the wallet from your home screen, launcher, app list, and recent apps. The only way to have your wallet appear is by calling a secret pin code.
BitLox is a bitcoin hardware wallet with a Privacy Set designed to ensure your anonymity. The hardware is capable of holding over 100 wallets with the ability to create millions of addresses for each wallet. You don’t need to worry about reusing addresses with the seemingly endless number of wallet/address combinations.
BitLox uses hidden wallets with data that is indistinguishable from random bytes to provide another layer of privacy and give you plausible deniability. The wallet also secures the signatures of your transactions with a NIST-certified true random number generator. And, if necessary, you can enter an emergency PIN to wipe all user data from the device.
If you’re interested in a secure, private hardware wallet, BitLox is a great option. Although more expensive than its competitors (the Extreme Privacy Set is $198).
Darkwallet was designed specifically to make your bitcoin use as private as possible. Their website states that the wallet is in its first public beta, but their GitHub page claims that the product is only in alpha.
The wallet is only available as a Google Chrome plug-in but includes features such as multisig and escrow support. To keep your transactions as anonymous as possible, Darkwallet uses a combination of stealth payments and CoinJoin compression.
Like most other anonymous wallets, Darkwallet generates a new public address for each transaction that you make.
Be aware that the wallet is operational, but full of bugs. On top of that, transactions through Darkwallet often take much longer than normal transactions on the bitcoin network.
Is the Dark Web Illegal?
We don’t want to leave you with the impression that everything on the underground web is nefarious or illegal. The TOR network began as an anonymous communications channel, and it still serves a valuable purpose in helping people communicate in environments that are hostile to free speech.
Is it legal to use TOR and similar browsers? Yes, such dedicated browsers are used by the military, police, journalists and whistleblowers to maintain their privacy online. TOR is free software and operates by concealing the user’s IP address, which prevents any personal data or metadata from being collected about the user. TOR can also be downloaded as an add-on for surface web browsers.
There’s material that you wouldn’t be surprised to find on the public web, such as links to full-text editions of hard-to-find books, collections of political news from mainstream websites and a guide to the steam tunnels under the Virginia Tech campus. You can conduct discussions about current events anonymously on Intel Exchange. There are several whistleblower sites, including a Dark Web version of Wikileaks. Pirate Bay, a BitTorrent site that law enforcement officials have repeatedly shut down, is alive and well there. Even Facebook has a Dark Web presence.
There’s also plenty of practical value for some organizations. Law enforcement agencies keep an ear to the ground on the Darknet looking for stolen data from recent security breaches that might lead to the perpetrators. Many mainstream media organizations monitor whistleblower sites looking for news.
On the other hand, due to the anonymity that TOR and similar private browsers offer, unfortunately, it is also a popular nesting ground for criminal and illegal activity. As such, weapons trading and drugs have appeared in marketplaces on the deep web. These illegal activities are classified to be in the ‘Dark Web’. While it is legal to access the deep web with a dedicated or anonymous browser, many websites on the deep web are not legal to visit.
Dangers of the Dark Web
While using the TOR browser to access the deep web, there is no guarantee that you are safe and fully anonymous. There have been numerous instances of de-anonymizing TOR users by the NSA in the US, and other government agencies. Due to the nature of the Deep and Dark Web, TOR users can often hack other users to find out more about them. So while it is legal to use, users should be cautious of the risks:
- First, there are a number of privacy concerns. Newbies to the underground web should know that they should always use a secure alias when registering a service on the underground networks. This means you need to create an entirely new and random name that is totally disconnected to your real identity, name, or email account. It’s very easy for someone to track you down if you use the same aliases on different networks or services. Furthermore, if you are a paying user, you should carefully weigh the option of using a payment card when conducting transactions. It all depends on what you’re buying. In general, however, Bitcoin is the standard payment method.
- Second, there’s computer security to think about. The Darknet is one of the main places where computer hackers, security experts, and other interested parties meet to discover, learn about, trade in, launch, and put a stop to digital attacks and crime. With that in mind, do not ever download binary files from untrusted sources, as they could be a conduit for dangerous new strains of malware. Some of the most popular and damaging malware have infected thousands of computers through the Dark Web before spreading to other machines via other networks and distribution methods. Don’t forget about the nonstop Darknet monitoring.
- Third, the TOR Browser is the most popular application used for accessing the underground web. But by itself, it’s not entirely secure. Over the years, there have been numerous vulnerabilities that have affected the security of TOR’s users and its nodes. Let’s be clear: TOR does not provide absolute anonymity or security,and users should not rely solely on it to safeguard themselves.
- Finally, in some cases, the Dark Web can also be damaging to your psychological state. Indeed, some of the underground communities can be a source of highly illegal materials, such as pornography and drugs. Coming into contact with these materials can have a negative effect on some people.
Summary
The Darknet is an excellent example of how difficult it is to prevent criminals from using anonymizing services designed to protect honest dissenters. TORs anonymizing functions are critically important to people who rely on it to discuss sensitive topics without fear of reprisal.
The Deep Web is becoming a household name, with more buyers than ever using their services. The future promises to be very interesting, with a push for a more regulated internet happening on the surface, while the Deep Web below thrives and gets more and more memes on the net.